Managed services are currently undergoing their biggest transformation since the emergence of the MSP model. MSPs are operating in an increasingly challenging environment – increasing competitive pressures, economic uncertainty and cyber security threats. In the face of these challenges, AI is becoming a key growth driver: up to 90% of MSPs consider AI solutions important or very important to their growth strategy. What’s more, most providers are already implementing AI in their operations – from infrastructure monitoring to customer service – redefining traditional service delivery models. This handout presents key trends and market data related to automation and AI in managed services, illustrating how the technology is changing MSPs’ efficiency, market dynamics and key areas of their business.
AI adoption trends in the SME sector
The percentage of companies declaring the use of AI in at least one business function increased from ~20% in 2017 to 78% in 2024. The rapid jump occurred especially between 2023 and 2024 due to the uptake of generative AI (pink line, 71% in 2024). For IT managers and service providers, this means that AI has become a common business tool on a global scale. This trend is also reflected in the SME industry – according to the survey, more than two-thirds of SMEs have implemented AI in areas such as systems monitoring or ticket automation. Importantly, the transformation is accelerating: in Q4 2023 alone. 62% of MSPs have expanded their use of AI, and analysts predict up to 11% growth in their revenues in 2024 thanks to these technologies. The world of managed services is thus entering a new era, where AI-supported automation is becoming the standard that defines competitiveness.
Impact of AI on service efficiency and quality
AI promises significant operational improvements for SME companies. By automating routine tasks and using machine learning, they can speed up responses and improve customer service. Suppliers report tangible benefits: AI-enhanced teams can handle more requests and issues in the same amount of time, reducing delays and errors.
Impact of AI implementation on the operational efficiency of the SME. The baseline (100) represents team productivity without AI support. The use of AI tools raises this indicator to ~120, representing a ~20% increase in productivity. This order of magnitude improvement translates into faster incident resolution and reduced operational costs. For example, the introduction of AI-based automation has reduced the average time to resolve a ticket by up to 68%, and operational costs have fallen by ~20%. This allows staff to focus on more complex tasks and proactive customer support, which increases customer satisfaction. As a result, MSPs using AI are seeing a marked increase in internal productivity and the quality of services provided, building a competitive advantage.
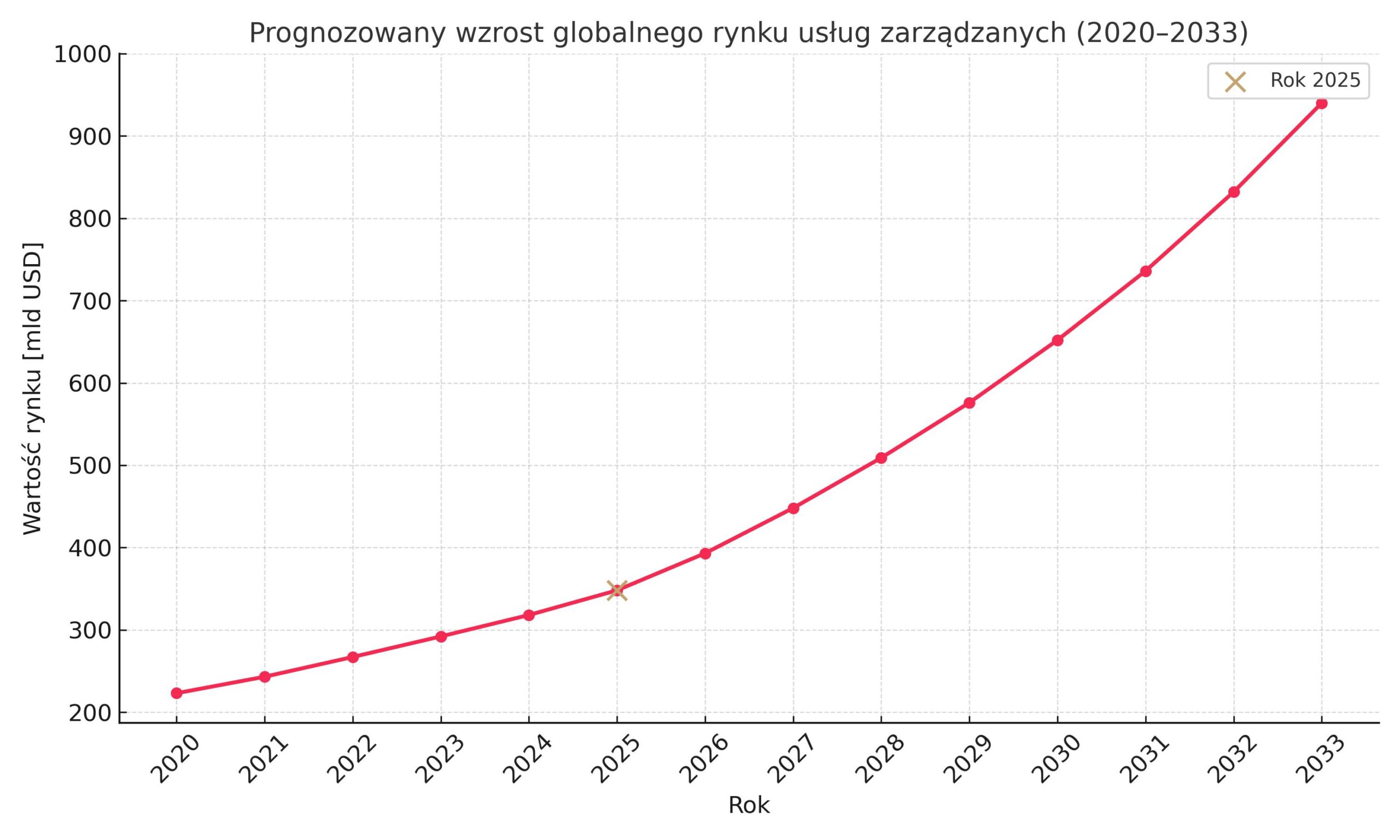
Market dynamics of managed services in the AI era
Automation is driving not only efficiency, but also growth in the overall SME market. More and more companies are opting to outsource managed IT services, expecting providers to use modern AI technologies for better performance. Global forecasts indicate a continued high growth rate for this industry in the coming years. The global managed services market is forecast to grow from approximately USD 348 billion in 2024 to approximately USD 393 billion in 2025 and over USD 1 trillion by 2033. By 2030, the market could already reach approximately USD 730 billion, representing high double-digit average annual growth. Such rapid expansion reflects the growing demand for specialised IT services delivered efficiently and at scale. Automation and AI are a key driver of this growth – streamlining the work of SMBs, enabling new services and business models, and attracting customers looking for innovative solutions. According to experts, AI is becoming one of the main drivers of managed services, and providers investing in these technologies can expect a greater share of the rapidly growing market.
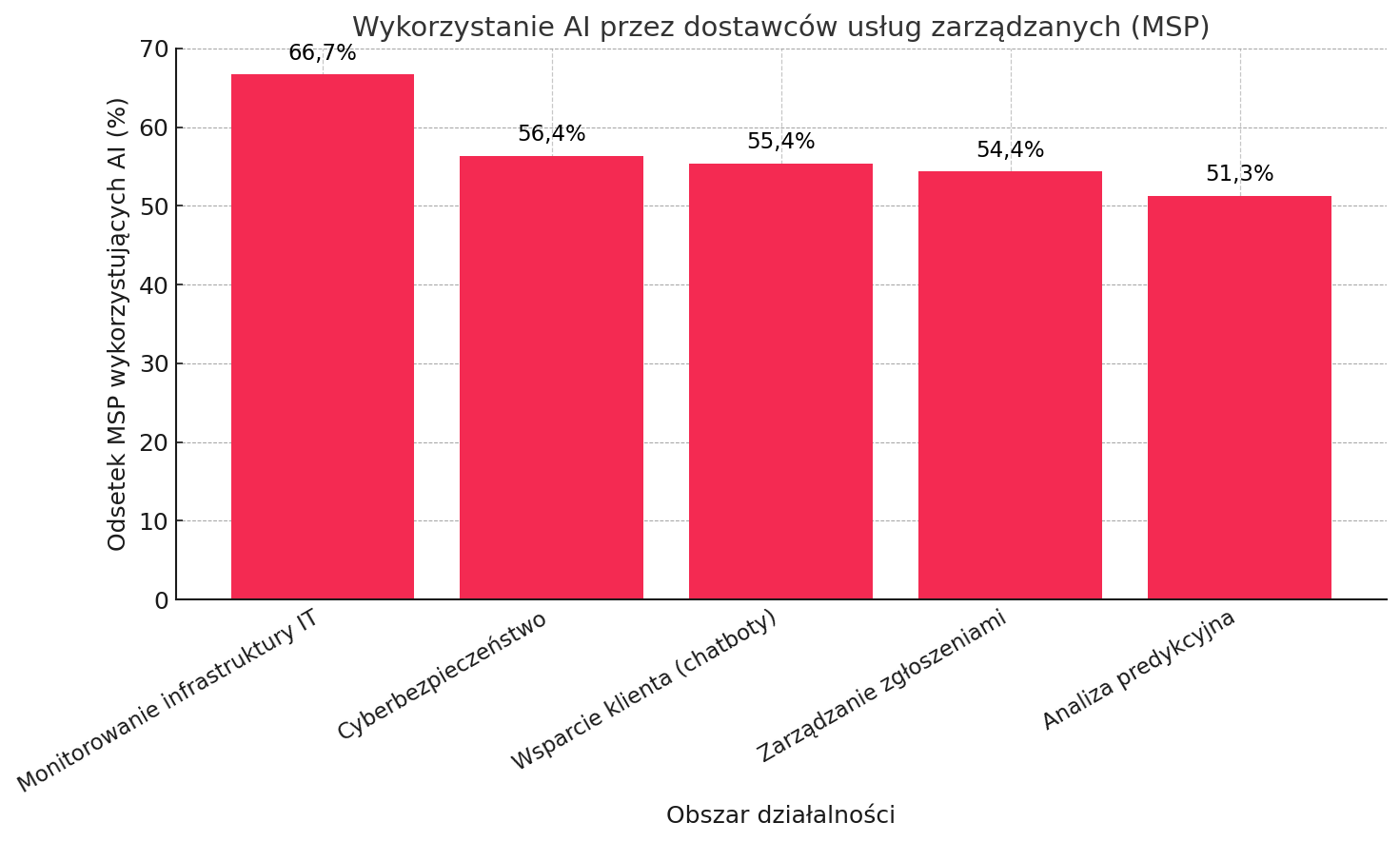
Key application areas for AI in SME services
AI is being applied to many aspects of managed service providers. The main domains in which automation and intelligent algorithms are changing the way MSPs deliver services, and the degree of adoption, are highlighted below. Percentage of MSPs using AI in different business domains. The most common use of AI is in infrastructure monitoring (67% of MSPs) and service request automation (54%). A slightly smaller percentage uses AI in the areas of cyber security (56%), customer support (chatbots – 55%) and predictive analytics (51% ). It is clear that IT systems monitoring and cyber security are at the forefront – AI here helps with 24/7 anomaly detection, threat detection and proactive incident response. Customer service automation (e.g. chatbots) relieves the burden on support teams, speeding up the resolution of common issues and improving customer satisfaction. Request and incident management gains agility thanks to AI – systems automatically categorise and prioritise tickets, reducing queues and response times. Predictive analytics tools, in turn, enable MSPs to predict failures or resource expansion needs before problems occur, minimising customer downtime.
As can be seen from the data above, AI-supported automation covers the full range of managed IT services processes – from the basics of infrastructure maintenance to advanced analytics. In each of these areas, AI not only improves efficiency (e.g. fewer alerts slipping through the cracks, fewer false alarms in the SOC), but also expands the range of services that MSPs can offer (e.g. predictive customer optimisation recommendations, intelligent advice through assistants). This shows that AI has become a versatile tool to improve MSP operations on many fronts simultaneously.
Challenges in implementing AI automation
Despite the obvious benefits, implementing AI in managed services brings with it a number of challenges. IT managers need to consider these when planning automation strategies to avoid pitfalls and maximise return on investment. The main obstacles include:
- Data quality and availability – AI requires large sets of reliable data to train models. Many companies struggle with scattered, incomplete or poor quality data, which limits the effectiveness of algorithms.
- Complexity of integration – Implementing AI into existing processes and systems can be difficult. It is necessary to adapt the IT infrastructure, integrate with a variety of tools and ensure that the new solutions are compatible with current procedures.
- Security and privacy – AI-based automation raises questions about data security (especially in the context of models that learn from customer data) and potential new attack vectors. MSPs need to ensure that the models they implement do not introduce additional security vulnerabilities.
- Skills gaps – Effective use of AI requires expertise that may be lacking in typical SME teams. The problem is a shortage of machine learning experts and the need to train staff to use the new tools.
- Costs and ROI – AI technology (from tool purchase to integration and maintenance) involves significant financial outlay. Companies must carefully calculate whether the expected improvements and savings will outweigh the costs incurred.
- Ethical aspects and regulatory compliance – With the increasing use of AI, issues of accountability of algorithms, transparency of decisions made by models and compliance with regulations (e.g. RODO for automated processing of personal data) arise. MSPs need to develop appropriate AI management policies to maintain customer trust and meet regulatory requirements.
Awareness of the above barriers is key to successful AI implementation. Technology leaders should prepare a comprehensive transformation plan, including phased implementation (e.g. piloting on a limited function), providing training for employees and selecting proven, secure AI solutions. This will ensure that automation becomes a permanent part of the MSP’s strategy and not just a one-off experiment.
Prospects for the future
Automation and AI are redefining the managed services model, but many changes are yet to come. In the coming years, expect the MSP offering to continue to evolve, with MSPs increasingly delivering AI-based services beyond the traditional framework. For example, the concepts of proactive, predictive services are already emerging: providers can anticipate customer needs and propose solutions before a problem arises (e.g. preventative upgrades before a failure occurs, automated suggestions for performance improvements). More integrated service platforms are also being developed, where the customer receives a personalised, adaptive set of managed services that adapt dynamically to their needs. All this means that MSPs that adopt AI quickly will gain an advantage. They will be able to offer innovative, higher value-added services that are difficult to achieve through traditional methods. In contrast, providers that delay investing in intelligent automation risk being left behind – their services may prove to be less efficient, more expensive and unable to meet growing customer expectations of proactivity and personalised service. As one industry report put it, this is only the beginning of the transformation: the most innovative MSPs will be able to provide services still unimaginable today, from ‘bespoke’ marketplaces that adapt to user needs to cyber security bordering on precognition (predicting and stopping breaches before they happen).
In summary, automation and AI are becoming the new face of managed services. What this means for IT managers and technology decision makers is the need to boldly but thoughtfully enter the world of AI – to harness its potential to increase efficiency and create new value for the business, while consciously managing the challenges. MSPs that successfully integrate AI into their offerings can bring service quality to unprecedented levels, shaping the future of the entire industry. Conversely, those who stay with old methods risk losing competitiveness in the face of the coming automated future of IT services.












